The Difference Between LCD and OLED Screens
With the continuous development of technology, smartphone vendors continue to upgrade their products in order to provide consumers with a better experience. As an indispensable electronic product in people’s daily life, mobile phones are used most frequently every day. Screens are crucial to consumers’ experience.
Currently, in the mobile phone screen industry, OLED and LCD are relatively common display technologies in the market, and both occupy a certain market share in the market. If you sell or repair phone screens, then you must know the difference between LCD and OLED screens, which can help you save costs and serve your customers better.
What is LCD
LCD is a liquid crystal display, which is a display that uses liquid crystal to control light transmittance technology to achieve color. LCDs are made of two flexible polarizing materials and a layer of liquid crystal solution, using a backlight or reflector to produce color or monochrome images. When an LCD is cracked, it cannot filter colors properly. What you see is not a range of colors, but an unfiltered backlight. Typically, on a phone, the LCD and touch layers are fused together and need to be replaced at the same time. That’s why either of them costs the same.
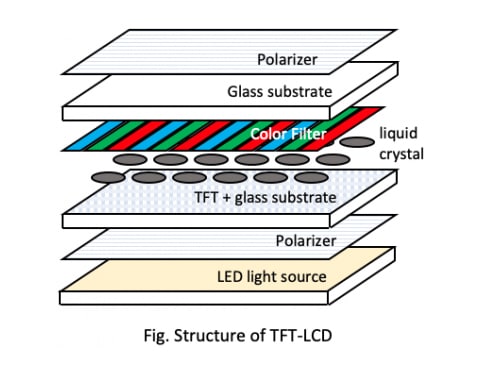
Pros & Cons of LCD on iPhones
Pros:
- Long lifetime: the backlight layer of LCD is used to emit light, other components are not easy to damage.
- More eye-friendly than OLED: LCD backlight is an independent white LED backlight, with no flicker, more eye-friendly.
- Cheaper than OLED
Cons:
- Thicker: In addition to the backlight layer and liquid crystal layer, the LCD screen also has some polarizers in the middle, so it is much thicker than OLED.
- Slow response time: The deflection of the liquid crystal layer is related to the temperature. The lower the temperature, the slower the deflection speed, so the LCD screen will have a very obvious smear phenomenon at low temperatures.
- High power consumption: As long as the LCD screen is turned on and the entire screen is fully lit, it will consume power all the time.
What is OLED
The full name of the OLED is Organic Light-Emitting Diode. OLED does not have a backlight layer, and each pixel can be independently controlled on and off, so it is not necessary to turn on the entire backlight layer like an LCD screen. When the phone is locked, some pixels can be lit up individually, and some important information such as time and notification can be displayed with low brightness and low refresh rate.
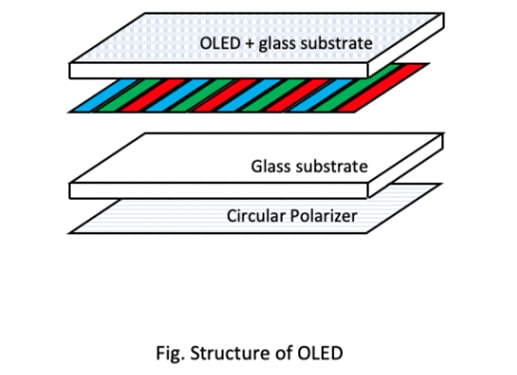
Pros & Cons of OLED on iPhones
Pros:
- Higher contrast: Contrast refers to the brightness ratio of black and white light and dark in the picture. OLED itself does not have a backlight, and each pixel is independently controlled, so the power supply to display black pixels can be directly cut off so that no light is emitted at all.
- Lower power consumption: OLED screen only consumes more power than LCD when it is turned on to display a pure white screen. Unless you’re stuck in white for a long time, OLED lasts longer.
- Faster response time: The OLED screen does not have a liquid crystal layer and is naturally not limited by the temperature of the liquid crystal layer. The OLED screen switches colors between colors, the response time is very short, and there is almost no smearing phenomenon.
- Thinner: OLED screens do not have a backlight layer and a liquid crystal layer, so they are very easy to make thin.
Cons:
- Shorter lifetime: Organic matter, frequent electron migration, and self-luminescence directly lead to the shorter lifespan of OLED screens than LCD screens.
- Hurts eyes: OLED can only use low-frequency PWM dimming. The general frequency is up to about 250Hz, and some visually sensitive people will notice it, which makes them more prone to visual fatigue.